Nanomembranes in waste water treatment
As we know that nanotechnology is a new science,
the way of filtering at the nanoscale level with the use of a membrane doesn’t
seem as anything brand new. It’s a biomimetic process Xeroxed up directly from
the nature.The living cells use a structure of the nanomembrane for
functioning. The processes include the conveying of salts from blood and also
the shifting of oxygen to and carbon dioxide from the cells.
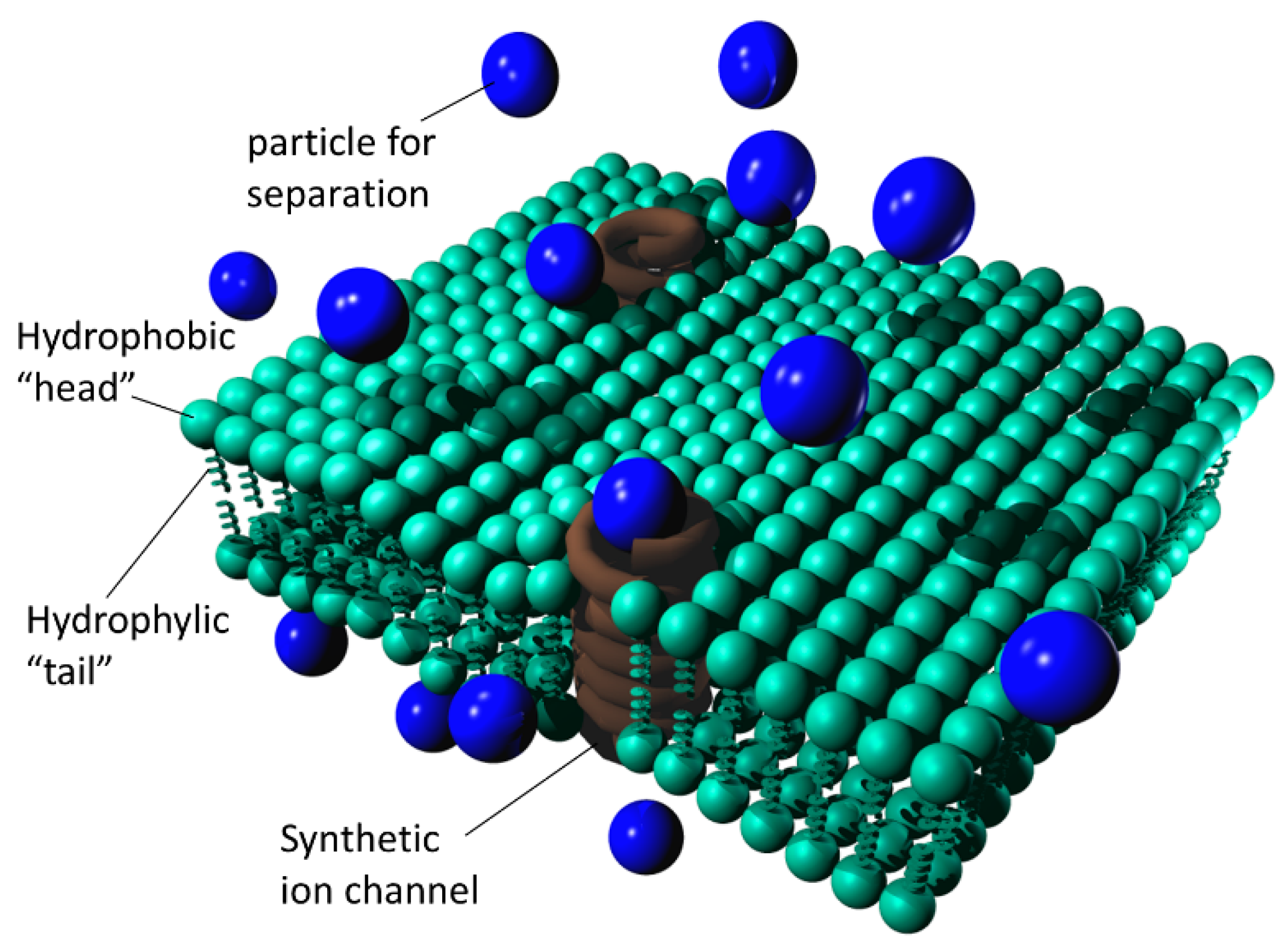
Nanomembranes are basically made from the organic
polymers based on nanocomposites having a thickness less than 100nm. Such
nanomembranes include organic polymers amalgamated with a mesh of
silica nanoparticles. The size of holes in the mesh restricts or allows the
passage of different sized molecules.
A special focus in BioSense research is the development and functionalization of nanomembranes for sensing applications. Due to very large aspect ratio of nanomembranes, such sensors imply very large active areas for a small volume, resulting in high sensitivity and miniature size of the final devices. This quality of nanomaterials is expressed in 0-D nanostructures (dots and cages) and 1-D structures (nanowires, nanotubes and nanochannels), as well as in 2-D structures like ultrathin films and nanomembranes. BioSense researchers develop various nanostructures as sensing elements which will allow the detection of ultra small concentrations of environmental pollutants, additives or toxins in the food chain, as well as the development of various sensors of complex analytes such as chemical and biochemical substances.
Applications for nanomembranes include :
• Desalination of sea water
• Purification of polluted water
• Removal of carbon dioxide and other pollutants from exhaust gases
• Sensors in MEMS

it seemed helpful
ReplyDeleteNiceeeeee
ReplyDelete